Weaknesses of FIFA’s Organization Structure
One of the most challenging things during the due diligence of a client is identifying beneficial owners of an entity and understanding potential weak points in the ownership chain of a company. This article aims to consolidate and show weaknesses of the FIFA’s organization structure that were exploited in the selfish interests of the executive committee members and WC hosting countries for decades.
An important role in determining where the next World Cup championship would take place was the Executive Committee (in 2016 reorganized to FIFA’s Council, which includes 37 members) of FIFA. It consisted of 24 members which included the President, General Secretary, 8 Vice Presidents and 15 members. 8 VCs and 15 members were coming from FIFA’s 6 confederations which represent different continents as shown in the Organization chart. Each executive member served a term of 4 years and could be reelected. Beside the executive committee, FIFA has a congress composed of 211 national associations. These national associations make up the 6 confederations. The congress meets annually and every 4 years elects the President of FIFA.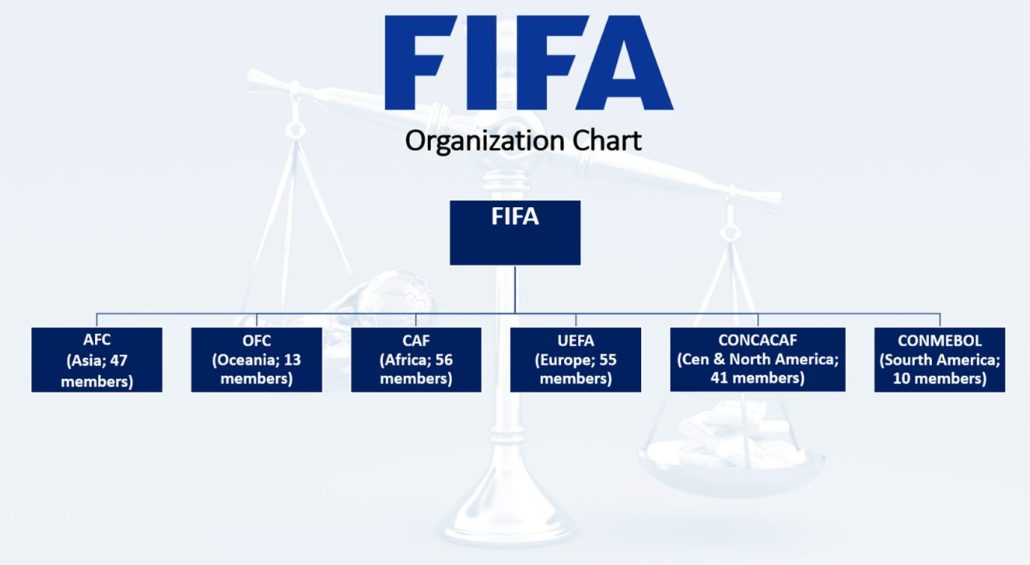
AFC – Asian Football Confederation
OFC – Oceania Football Confederation
CAF – Confederation of African Football
UEFA – Union of European Football Associations
CONCACAF – Confederation of North, Central American and Caribbean Association Football
CONMEBOL – Confederation Sudamericana de Futbol
Every 4 years, the Executive Committee chooses the hosting country for the World Cup. In 2004, there were two candidates for hosting the WC 2010; Morocco and South Africa. According to investigative journalists, South Africa paid $10 million to the Vice President of FIFA from CONCACAF to secure the votes (CONCACAF had 3 voting rights on the executive committee of FIFA) for hosting WC 2010. 10% of the $10 million transferred to the former vice president of the US Soccer Federation. A similar strategy was used by Qatar to win the bid for the WC 2022. Three CAF voting members were bribed for $1-5 million each to get their votes.
Other scandals show how the former president and some vice presidents of FIFA were bribing other executive members of confederations to get elected as President of FIFA. In the book by Mr. Yallop “How they stole the Game” reported how FIFA’s former president engineered a victory over Mr. Johansson by buying votes with envelopes of cash. Later in 2011, the same tactic was used by another FIFA member of the executive committee to save votes of Caribbean officials to get elected as President of FIFA.
Thus, these cases show how the officials and executives on the periphery of the FIFA organization were exploited in their own interests. It is important to identify and understand every chain in the ownership structure to prevent illegal activities by organizations and companies.
#AML #KYC #Compliance #Regulatory #Source of Funds #FIFA #Qatar #WorldCup #Luxemburg #Germany #Switzerland
#Curentis AG



