Banking is data - Automating data mapping (modeling) with tools and AI
Data mapping as a central part of data management is a time-consuming and therefore costly task in many banking projects.
In this article, CURENTIS describes the challenges of data mapping and considers whether the application of tools and AI technologies can be used to automate the process of data mapping or modeling.
What does data mapping mean in the context of data management?
Data management is a broad term that refers to the management of data in a structured, efficient and secure way. The term "data mapping" refers to how data is brought together between different systems, formats or structures. This includes various aspects, from the definition of databases and tables to the organization, maintenance, security and analysis of data.
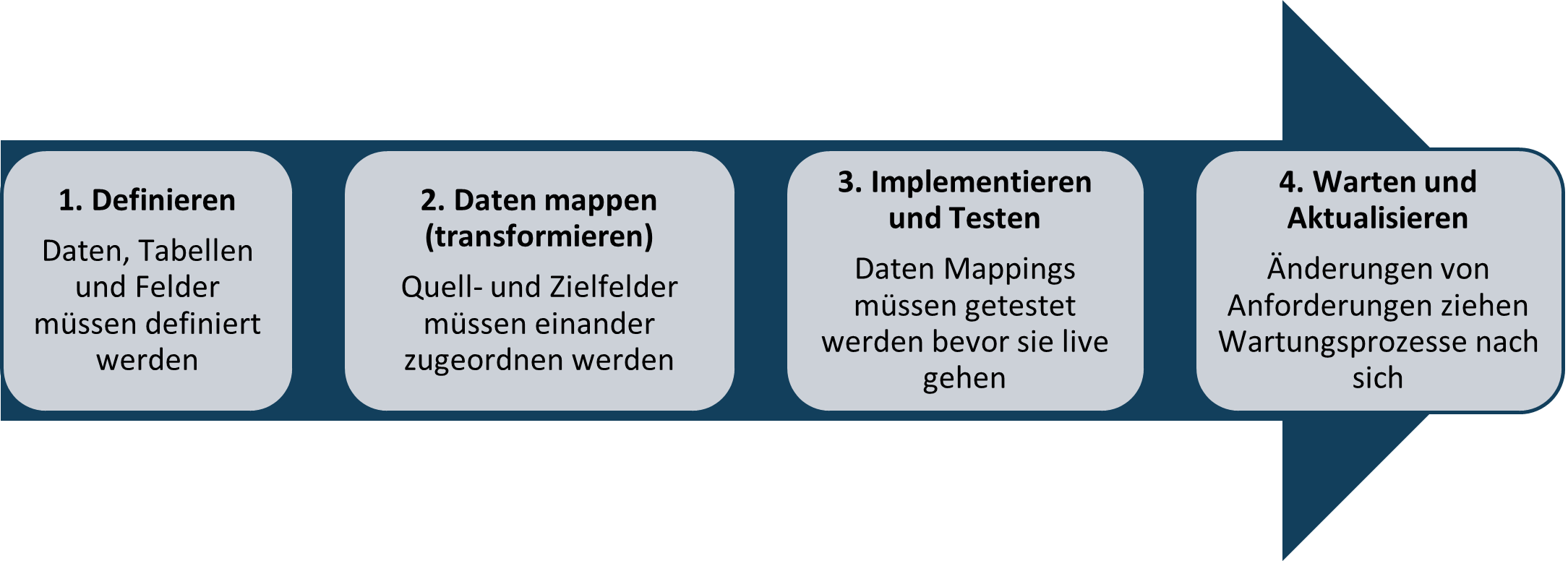
The following graphic illustrates the data mapping process:
1. define
Before data mapping is implemented, data identification and the definition of tables and databases are carried out. The first step is to identify the types of data that are transferred between different systems or within the same system. The second step is to determine the tables and databases that contain the relevant data. This can include both the source and target tables in a database migration scenario.
2. mapping data
Data mapping refers to the process of transferring or transforming data from one data model to another. This is often done as part of data integration, migration or transformation processes. The aim of data mapping is to ensure that data can be transferred correctly and consistently from a source system to a target system.
3. implementation and testing
Once the data mapping has been designed, implementation and testing follow. Based on the data mapping design, scripts or programs are created to transfer the data from the source to the target environment. This may involve the use of ETL (extraction, transformation, loading) tools, scripting languages such as Python or specialized data integration tools.
4. Waiting and updating
It is important that changes to data requirements are carefully managed and documented, as up-to-date documentation can have a significant impact on the integrity of the data and the functioning of the system. Effective version control and documentation are therefore crucial to ensure consistent and reliable data mapping, especially in environments with changing requirements. Every change entails maintenance and update processes.
A well-designed data model forms the basis for databases and makes it possible to store, retrieve and maintain data efficiently. It also facilitates communication between different stakeholders, including database developers, analysts and end users.
How will the automation of this process be improved through the use of specialized tools and AI algorithms?
- Automation: The process of creating and updating data mappings is automated to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
- Data modeling: The creation of models that describe how data is mapped between different sources and destinations is automated.
- Tools: Special software tools are used to reduce or eliminate the manual effort and error rate in data modeling.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Advanced artificial intelligence algorithms are integrated to recognize patterns, learn automatically and suggest or create more precise data associations.
The automation of data mapping (modeling) in banks using tools and artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the use of technologies to automate the process of mapping data between different systems, formats or structures.
What are the known advantages of choosing tools in the process of data mapping in the context of banks?
- Increased efficiency: By using automated tools and AI algorithms, banks can speed up the process of data allocation. This leads to a significant increase in efficiency, as manual allocations are often time-consuming.
- Accuracy and precision: AI algorithms can recognize patterns in large data sets and automatically create precise mappings. This helps to minimize human error and improve the accuracy of data mapping.
- Handling large volumes of data: In the banking industry, there are often large amounts of data that need to be exchanged between different systems. Automation with AI makes it possible to process this data on a large scale.
- Adaptability to change: Banking data can change due to changes in regulatory requirements or business processes. AI can help to ensure that automated mappings can adapt to such changes.
- Risk mitigation: By automating data mapping, banks can reduce the risk of human error, especially when handling sensitive financial data.
- Faster response to market requirements: The ability to update data mappings quickly and accurately allows banks to be more agile in responding to changing market conditions.
- Fulfillment of compliance requirements: Banks are subject to strict compliance requirements. Automating data mapping can help to ensure that data is mapped correctly according to regulatory standards.
- Improve customer experience: Accurate data mapping is critical to an improved customer experience. Through automation, banks can ensure that customer information is managed accurately and consistently.
- Integration of data sources: Banks often use different systems and sources. Automation helps to ensure seamless integration between these different data sources.
The use of mapping tools, especially those that use artificial intelligence (AI), can offer numerous benefits, but there are also potential dangers and risks that should be considered. Here are some of the potential challenges:
- Incorrect mappings: AI-based mapping tools can make incorrect assignments due to insufficient training data or complex data structures. This can lead to data inconsistencies and incorrect results.
- Uncertainty in decision-making: AI models are often designed as "black boxes", which means that their decision-making processes are difficult to understand. This can create uncertainty about how certain mappings come about and how they can be improved or remedied.
- Data protection and security concerns: The use of AI tools in the mapping process often requires access to sensitive data. Privacy and security concerns can arise, especially if the data is not adequately protected during the mapping process.
- Dependence on training data: The performance of AI models depends heavily on the quality and representativeness of the training data. If this data is distorted or incomplete, the models can be prone to errors and make poor decisions.
- Complexity of data structures: AI tools can have difficulties processing complex data structures or unstructured data appropriately. This is particularly relevant when it comes to the correct assignment of data fields in different formats.
- Lack of robustness to changes: Changes in data structures or data format can cause AI models to lose their accuracy if they are not regularly updated or retrained.
- Lack of consideration of business rules: AI models may not adequately address business rules or industry-specific requirements. This can lead to problems when it comes to adhering to compliance regulations or specific company guidelines.
- Ethics and bias: If the training data contains bias or discrimination, AI models can adopt these biases. This could lead to unethical decisions or actions, especially when it comes to sensitive information or personalized data.
To meet these challenges, it is important to use AI tools responsibly. This includes monitoring results, continuously improving models, transparency in decision-making processes and compliance with data protection and security standards. It is also advisable to integrate human review and expert knowledge into the mapping process to minimize potential risks.
Following the advantages and disadvantages of using AI in the context of automated mapping processes, the most popular mapping tools on the market are presented below and their purpose briefly described:
- Talend Open Studio: (free open source software): Designed for integration of data sources. It offers a graphical user interface that allows users to connect data sources and perform complex transformations.
- Informatica PowerCenter (Enterprise ETL tool): Designed for the integration of data from different sources. It offers a wide range of functions and a simple user interface to simplify mapping.
- FME (Feature Manipulation Engine): (powerful mapping tool) Designed for the integration of geodata. It offers a wide range of functions, including the ability to convert and transform geodata in various formats.
- Apache Nifi: (open source system for data integration): Designed for the management of data flows. It offers a wide range of functions, including the ability to transform data in real time.
- Altova MapForce: (visual mapping tool): Designed for integrating data from multiple sources. It offers a user-friendly graphical user interface
Overall, automating data mapping in banks helps to optimize data processing, ensure accuracy and improve agility in a rapidly changing financial environment. However, on the other hand, the challenges of automating data mapping exist, which is why it is important to use AI tools responsibly.
In view of the specialist content presented, CURENTIS works on advisory and conceptual solutions and actively supports customers in this complex subject area.